Ethereum Smart Contract In Blockchain Unlocking Potential
Ethereum smart contract in blockchain is not just a buzzword; it's the key to revolutionizing how we interact with technology and each other. These self-executing contracts, embedded with agreements directly written into code, promise to automate processes and eliminate intermediaries in various sectors. In a world increasingly driven by decentralization, understanding the intricacies of Ethereum smart contracts is essential for anyone looking to navigate the future of digital transactions.
At its core, Ethereum serves as a platform that enables developers to create smart contracts that run on its blockchain, providing transparency and security. By leveraging the power of the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), these contracts can execute automatically when predetermined conditions are met, fundamentally changing the landscape of digital agreements and decentralized applications (dApps).
Introduction to Ethereum Smart Contracts
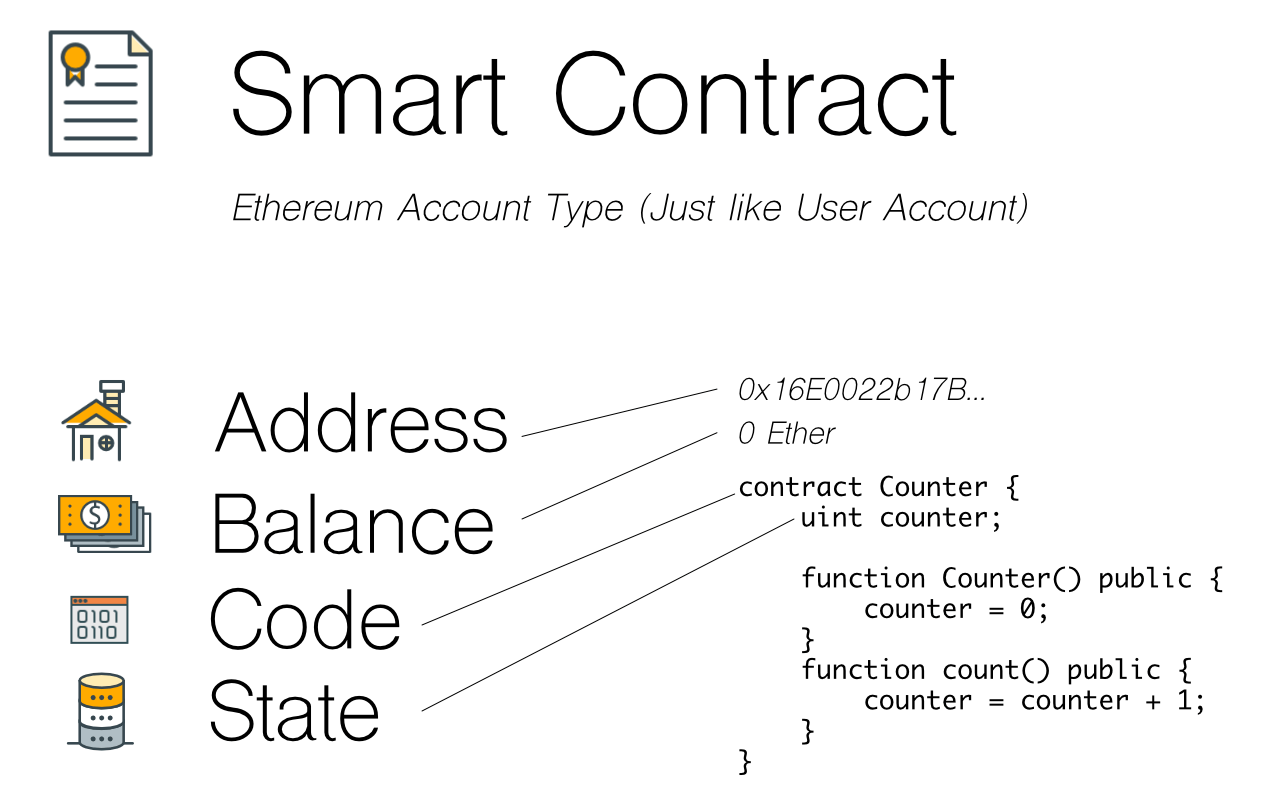
Ethereum is a groundbreaking platform in the realm of blockchain technology, allowing developers to create decentralized applications (dApps) that run on its network. At the core of Ethereum's functionality are smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These smart contracts enable automated, trustless transactions between parties, eliminating the need for intermediaries.Smart contracts hold significant importance in the development of dApps as they facilitate transactions and interactions without the need for a central authority.
This decentralization fosters transparency and security, making it easier for users to trust the system. In essence, smart contracts are the backbone of Ethereum's decentralized ecosystem, empowering various use cases across multiple industries.
Technical Framework of Ethereum Smart Contracts

To create smart contracts on the Ethereum network, developers primarily use a programming language called Solidity. Solidity is designed to enable the creation of complex smart contract logic, making it a preferred choice for Ethereum developers. The architecture of Ethereum itself is instrumental in supporting these contracts; it operates on a decentralized network of nodes that validates and records transactions on the blockchain.The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) plays a critical role in executing smart contracts.
It acts as a runtime environment that processes the code of the smart contracts, ensuring that they function as intended. The EVM is crucial for maintaining the integrity and security of the Ethereum network, allowing it to handle numerous transactions without compromising on performance.
Development Process of Ethereum Smart Contracts
Creating a smart contract involves several key steps from concept to deployment. The process typically includes:
- Defining the contract's purpose and functionality.
- Writing the contract code using Solidity.
- Testing the contract in a development environment to identify and fix any issues.
- Deploying the contract onto the Ethereum blockchain.
Several tools and platforms streamline the development of Ethereum smart contracts, with Remix and Truffle being popular choices. Remix is an online IDE that allows developers to write, test, and debug smart contracts directly in the browser. Truffle, on the other hand, offers a suite of tools for managing smart contract deployments and testing.Adhering to best practices is essential for ensuring the reliability and security of smart contracts.
Developers should conduct thorough testing, including unit tests and integration tests, to identify vulnerabilities before deployment.
Use Cases of Ethereum Smart Contracts
Ethereum smart contracts have found applications across various industries, each benefiting from their unique capabilities. Some notable sectors include:
- Finance, where smart contracts facilitate automated transactions and reduce the need for intermediaries.
- Supply chain management, enabling enhanced transparency and tracking of goods.
- Real estate, streamlining property transactions through automated, trustless agreements.
In the realm of real estate, smart contracts can revolutionize transactions by ensuring secure, transparent transfers of ownership without the need for traditional escrow services. Successful projects leveraging Ethereum smart contracts, such as Cryptokitties and DeFi platforms like Uniswap, exemplify the potential of this technology in creating innovative solutions.
Security Considerations for Ethereum Smart Contracts
As with any technology, security is paramount when it comes to Ethereum smart contracts. Common vulnerabilities include reentrancy attacks, integer overflow, and improper access control. Mitigating these risks requires diligent coding practices and thorough testing.The importance of security audits and code reviews cannot be overstated. Regular audits help identify potential vulnerabilities, ensuring that contracts are robust and secure before deployment.
Developers can follow a checklist to enhance the security of their smart contracts, which includes:
- Conducting thorough testing and vulnerability assessments.
- Implementing best coding practices.
- Engaging in code reviews with peers.
Future of Ethereum Smart Contracts
The future of smart contract technology looks promising, with potential advancements that could further enhance their functionality and security. Innovations such as layer 2 solutions aim to improve blockchain scalability, allowing Ethereum smart contracts to handle more transactions efficiently.As the Ethereum network evolves, so too will its smart contracts. Predictions suggest an increase in interoperability between different blockchain platforms, enabling seamless interactions across ecosystems.
This could lead to broader adoption of smart contracts in various sectors, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs in business operations.
Comparison of Ethereum Smart Contracts with Other Blockchain Platforms
While Ethereum remains a leader in smart contract development, other blockchain platforms like Binance Smart Chain and Solana also offer competitive features. A comparison of these platforms reveals both advantages and disadvantages.
| Feature | Ethereum | Binance Smart Chain | Solana |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transaction Speed | 15-30 seconds | 3 seconds | 400 milliseconds |
| Transaction Fees | Higher | Lower | Low |
| Programming Capabilities | Solidity | Solidity | Rust, C, C++ |
While Ethereum offers a robust ecosystem and extensive developer support, alternatives like Binance Smart Chain and Solana provide lower fees and faster transaction speeds. Each platform has its unique strengths, making the choice of blockchain dependent on specific project requirements and goals.
Ending Remarks

In conclusion, the versatility and potential of Ethereum smart contracts in blockchain continue to expand, offering innovative solutions across various industries. As we move towards a more decentralized future, understanding these contracts and their implications will be crucial. With ongoing advancements in security, scalability, and functionality, the future of Ethereum and its smart contracts remains bright and full of possibilities.
Question Bank
What is the main function of an Ethereum smart contract?
The main function of an Ethereum smart contract is to automate and enforce agreements between parties without the need for intermediaries, using code to execute predetermined actions once conditions are met.
What programming language is primarily used for Ethereum smart contracts?
Solidity is the primary programming language used for writing Ethereum smart contracts, designed specifically for the Ethereum blockchain.
How are Ethereum smart contracts tested for security?
Ethereum smart contracts are tested for security through rigorous code reviews, security audits, and automated testing frameworks to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities before deployment.
What are the common vulnerabilities in Ethereum smart contracts?
Common vulnerabilities include reentrancy attacks, gas limit issues, and improper access controls, which can lead to security breaches or loss of funds.
Can Ethereum smart contracts be modified after deployment?
Once deployed, Ethereum smart contracts are immutable; however, developers can design upgradeable contracts that allow for changes through specific mechanisms.

