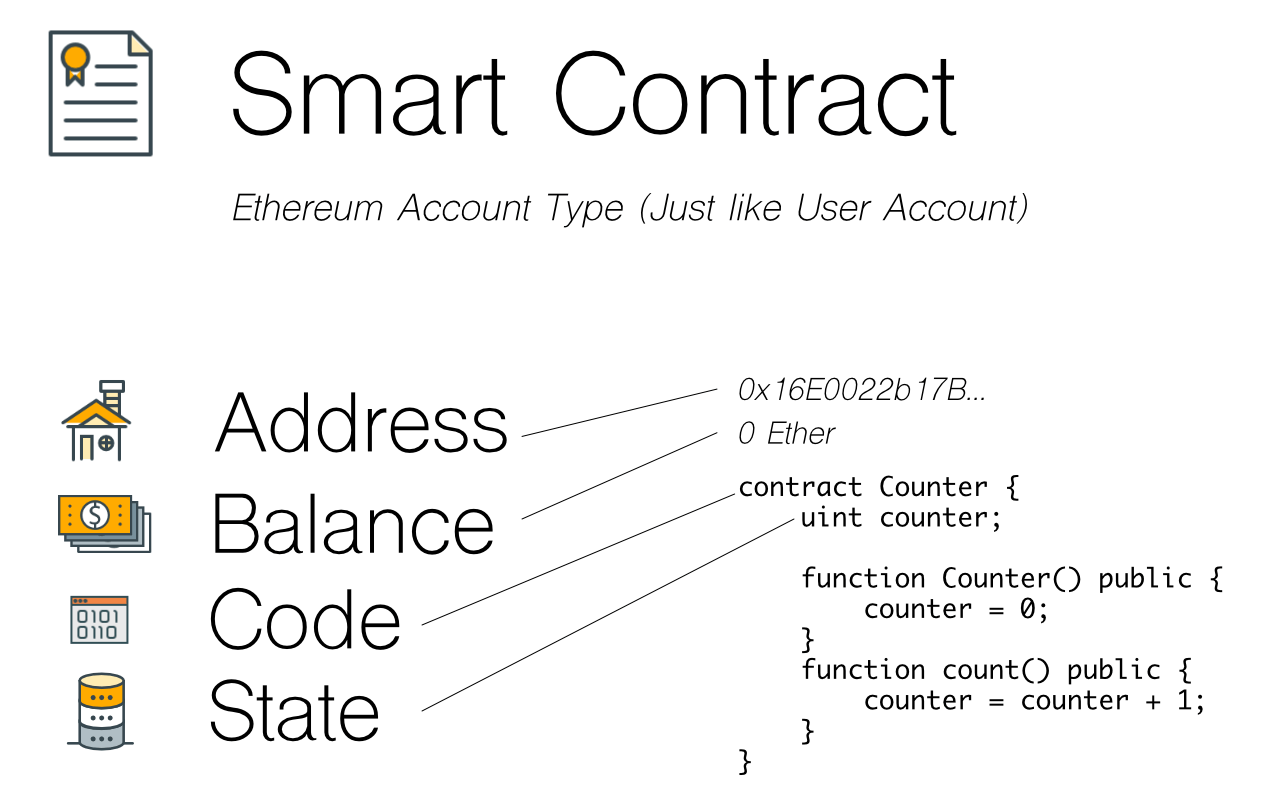
What Is Blockchain Architecture Understanding Its Essence
What is blockchain architecture, you ask? It's a fascinating realm at the intersection of technology and innovation, shaping the future of various industries. Understanding blockchain architecture is essential as it defines how decentralized networks operate, ensuring transparency, security, and efficiency. This exploration of its core components and significance highlights the transformative potential of blockchain across multiple sectors.
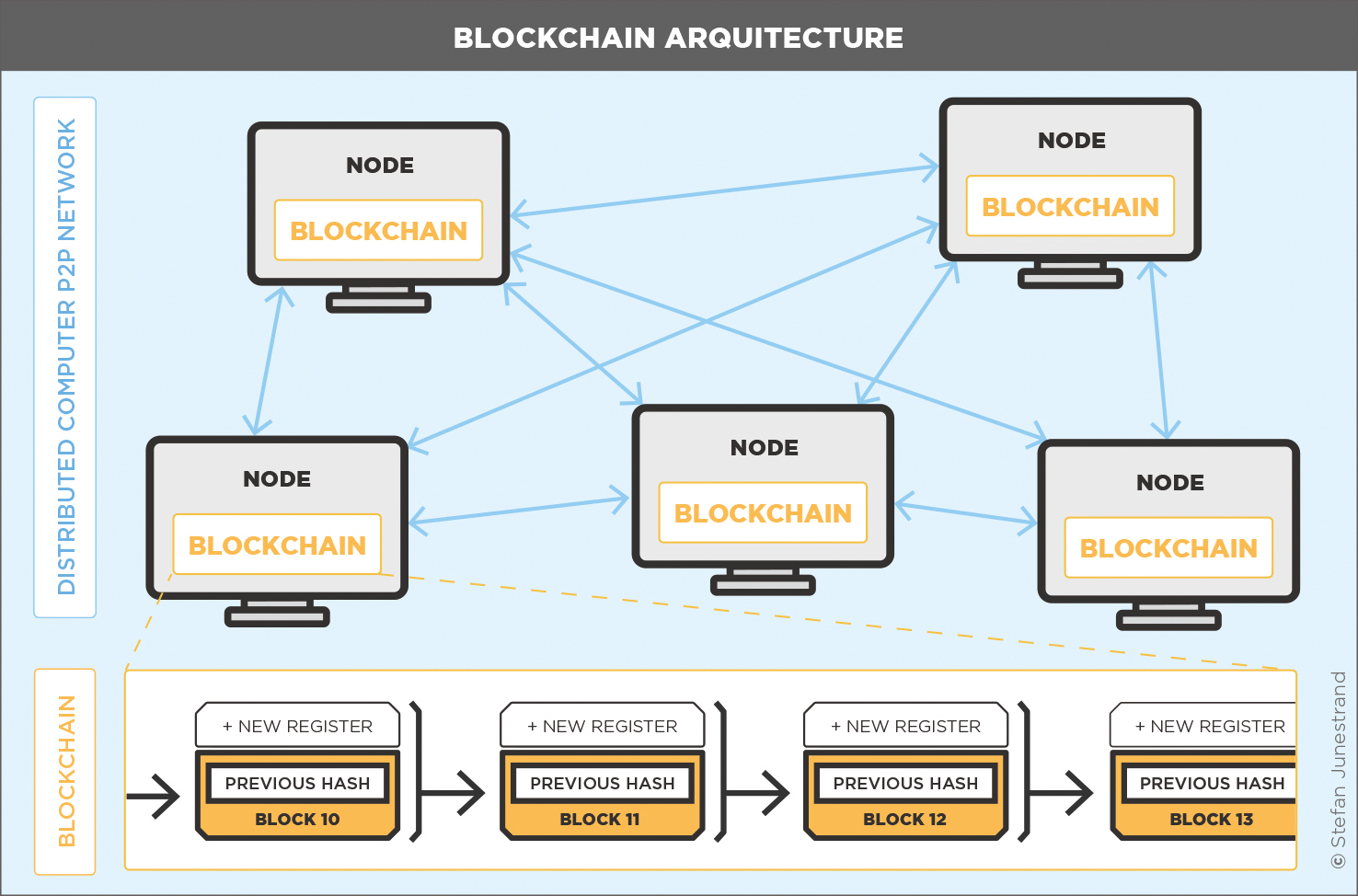
The architecture comprises crucial elements such as nodes, ledgers, and consensus mechanisms, each playing a vital role in maintaining data integrity and facilitating transactions. Recognizing these components opens a window to the advantages they offer, from enhancing security to improving efficiency in business operations.
Introduction to Blockchain Architecture
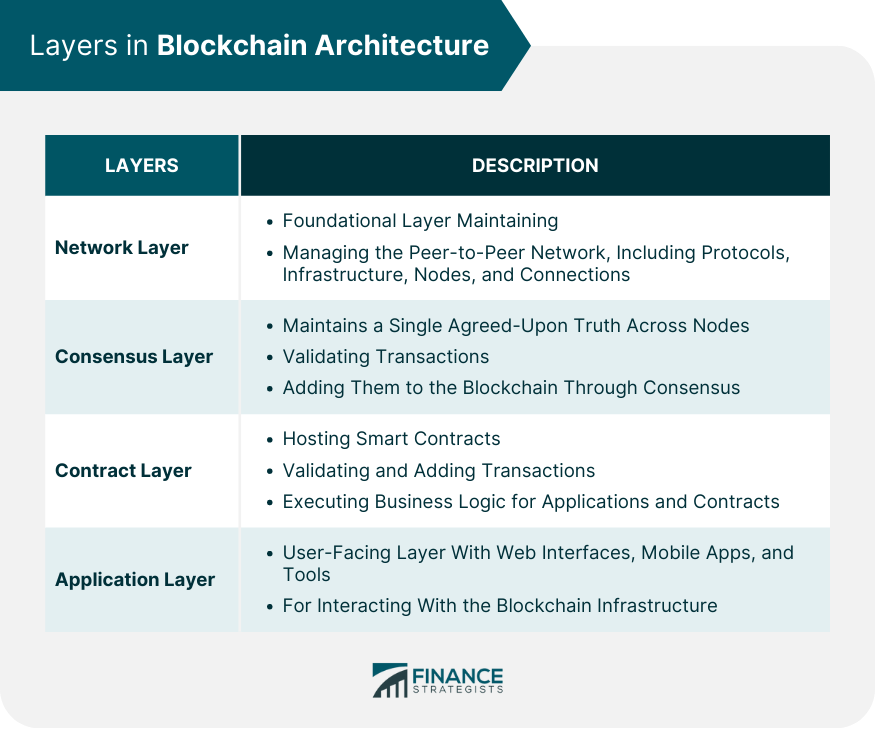
Blockchain architecture is a fundamental framework that underpins blockchain technology, influencing how data is stored, shared, and secured across diverse applications. Its significance is profound as it facilitates decentralized, transparent, and secure transactions, making it a transformative force in various sectors including finance, healthcare, and supply chain management. By understanding blockchain architecture, industries can leverage its unique capabilities to innovate and enhance operational efficiencies.The core components of blockchain architecture consist of nodes, ledgers, consensus mechanisms, and protocols.
Nodes act as individual participants within the network, while ledgers serve as records of all transactions, ensuring data integrity. Consensus mechanisms, on the other hand, validate transactions to maintain the network's reliability. Grasping these components allows stakeholders to implement blockchain solutions effectively, aligning with specific business needs.
Key Components of Blockchain Architecture
Nodes in a blockchain network are critical as they facilitate communication and transaction processing. Each node maintains a copy of the entire blockchain, ensuring redundancy and resilience. There are different types of nodes, including full nodes that store the complete history of the blockchain and lightweight nodes that only keep the necessary data for transaction verification.Ledgers play a pivotal role in maintaining data integrity.
They provide a tamper-proof record of all transactions, as each entry is linked to the previous one using cryptographic techniques. This structure ensures that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered without consensus from the network, thus preserving trust among participants.Consensus mechanisms are essential for validating transactions and preventing double-spending. These mechanisms—such as Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, and Delegated Proof of Stake—determine how transactions are approved and added to the blockchain, impacting the speed and security of the network.
Types of Blockchain Architecture
There are three primary types of blockchain architectures: public, private, and consortium blockchains. Each serves different purposes and has unique characteristics.
- Public Blockchain: Open to everyone, allowing anyone to participate in the network. Examples include Bitcoin and Ethereum, which are utilized for cryptocurrency transactions and smart contracts.
- Private Blockchain: Restricted access for a limited number of participants. These are often used by businesses for internal processes, enhancing privacy and control over shared data.
- Consortium Blockchain: A hybrid approach where multiple organizations share control, ideal for industries requiring collaboration, such as banking and supply chain sectors.
Each type of blockchain architecture addresses specific needs and challenges, facilitating diverse applications from digital currencies to supply chain transparency.
Blockchain Protocols
Blockchain protocols are crucial as they define the rules and structure governing blockchain operations. They determine the mechanisms for transaction validation, data transmission, and network security. Notable protocols include Bitcoin, which employs Proof of Work for transaction verification, and Ethereum, which supports smart contracts through its own protocol.Protocols greatly influence transaction speed and security. For instance, Bitcoin's block time averages around 10 minutes, while Ethereum's is approximately 15 seconds, showcasing a significant difference in how quickly transactions can be confirmed.
In contrast, Hyperledger frameworks are designed for enterprise solutions, emphasizing privacy and performance tailored for specific business cases.
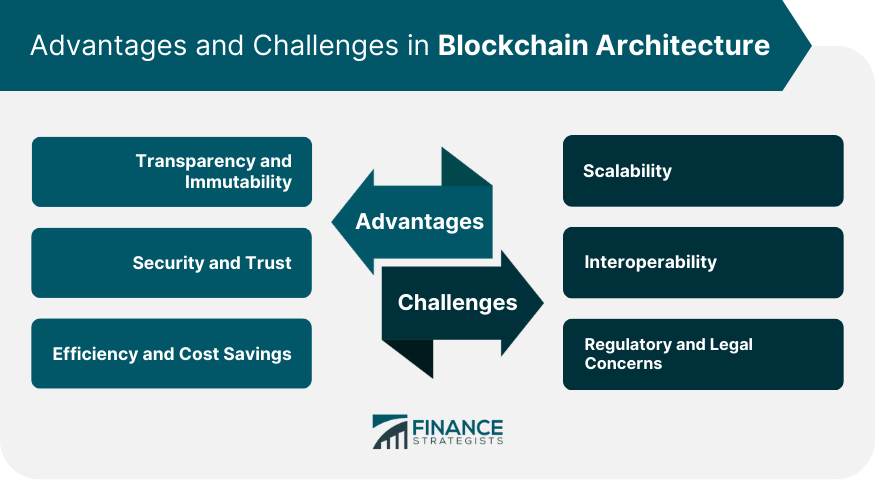
Scalability and Security in Blockchain Architecture
Scalability remains a significant challenge in blockchain systems, particularly as transaction volumes increase. Solutions like sharding and layer 2 protocols, such as the Lightning Network for Bitcoin, aim to improve scalability by processing transactions off the main blockchain while still ensuring security.Security is paramount in blockchain architecture. Techniques such as cryptographic hashing, multi-signature wallets, and decentralized consensus contribute to securing the network against threats.
However, a trade-off often exists between scalability and decentralization, as increasing one may compromise the other, which businesses must carefully navigate.
Future Trends in Blockchain Architecture
Emerging trends in blockchain technology include advancements in interoperability, allowing different blockchain networks to communicate and share data seamlessly. Additionally, the integration of blockchain with artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) creates new opportunities for automation and data analytics within decentralized systems.Potential innovations could reshape blockchain architecture by introducing more efficient consensus algorithms and enhancing user privacy.
As industries explore these trends, the influence of blockchain is expected to expand, driving digital transformation across sectors.
Use Cases and Applications
Real-world applications of blockchain architecture are diverse and impactful. In finance, decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms leverage blockchain for lending and borrowing without intermediaries. Healthcare utilizes blockchain for secure patient data sharing, ensuring privacy and regulatory compliance.Various sectors are harnessing blockchain for tailored solutions, including supply chain management, where companies like Walmart track food products to ensure safety and authenticity. While the benefits of transparency and efficiency are significant, challenges such as regulatory compliance and technological integration can pose obstacles in these applications.
Final Summary
In summary, the exploration of blockchain architecture reveals its critical role in shaping the technological landscape. As we delve into its various components and types, it becomes clear that understanding this architecture is not just for tech enthusiasts but for anyone looking to grasp the future of digital transactions. Embracing these insights will empower industries to navigate the evolving world of blockchain effectively.
Clarifying Questions
What is the purpose of blockchain architecture?
The purpose of blockchain architecture is to provide a framework that ensures secure, transparent, and efficient transaction processing in a decentralized network.
How does blockchain architecture differ from traditional databases?
Unlike traditional databases, which are centralized and controlled by a single entity, blockchain architecture is decentralized and allows multiple parties to maintain and verify the database collaboratively.
Can blockchain architecture be used in industries beyond finance?
Yes, blockchain architecture has applications in various industries, including healthcare, supply chain, and voting systems, among others, due to its ability to enhance transparency and security.
What are the main challenges facing blockchain architecture?
Key challenges include scalability, energy consumption, and integration with existing systems, which need to be addressed for broader adoption.
How does consensus mechanism affect blockchain performance?
The consensus mechanism determines how transactions are validated and added to the blockchain, impacting speed, efficiency, and security within the network.